Understanding Steel Fabrication
What is Steel Fabrication?
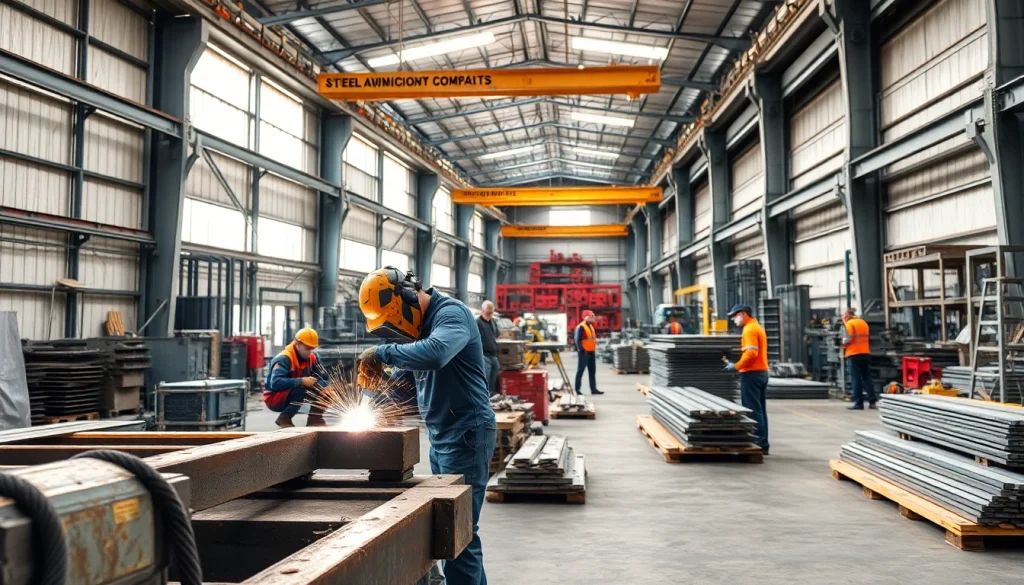
Steel fabrication is the process of cutting, bending, and assembling steel structures or components from raw materials. This entire process begins with raw steel, which is transformed into functional items using various techniques such as welding, machining, and forming. Steel fabrication shops play a vital role in manufacturing buildings, bridges, and various products that require strong and durable materials. The skilled workforce in these shops utilizes precision engineering techniques to ensure that projects meet design specifications and safety standards. A thorough understanding of this process, alongside the infrastructure of a steel fabrication shop, is essential for anyone looking to utilize fabricated steel in projects.
Types of Steel Fabrication Services
Steel fabrication services can be broadly classified into several categories, including structural fabrication, sheet metal fabrication, and custom fabrication.
- Structural Fabrication: This involves creating steel structures such as beams, columns, and trusses commonly used in construction projects. Structural fabricators work closely with architects and engineers to ensure that their designs are realized accurately.
- Sheet Metal Fabrication: A process that includes cutting and shaping sheet metal into desired forms and features. Services like bending, punching, and laser cutting are utilized to produce parts for ventilation, enclosures, and various industrial applications.
- Custom Fabrication: Tailored services to meet unique project specifications. Custom fabricators can design and manufacture components that fit specific applications, whether for specialized machinery or custom furniture.
Common Applications of Steel Fabrication
Steel fabrication is used across a multitude of industries, showcasing its versatility and strength. Some common applications include:
- Construction: Steel beams and columns form the framework of high-rise buildings and bridges, providing essential structural support.
- Automotive: Various steel components are fabricated for vehicles, contributing to the overall strength and safety of automobiles.
- Aerospace: The aviation industry uses precision-fabricated parts for aircraft, ensuring safety and performance in demanding environments.
- Manufacturing: Many manufacturing processes rely on fabricated metal parts to create machinery and tools needed for production.
Selecting the Ideal Steel Fabrication Shop
Key Factors to Consider
Choosing the right steel fabrication shop is crucial for the success of your project. Key factors to consider include:
- Experience and Expertise: Investigate the shop’s experience in handling projects similar to yours, as seasoned professionals bring invaluable insights and problem-solving ability to the table.
- Technology and Equipment: Inquire about the technology and equipment used in the shop. Shops that invest in modern machinery are often more capable of delivering precise and efficient fabrication services.
- Location: Proximity can affect shipping costs and lead times. Choosing a shop closer to your project site could result in faster turnaround times.
Evaluating Shop Capabilities
When evaluating a fabrication shop, certain capabilities can indicate whether it’ll meet your needs:
- Diverse Services: A shop offering a range of services, including welding, machining, and surface treatment, can be more helpful than one specializing only in one area.
- Customized Solutions: The ability to customize and adapt processes to meet distinct project requirements is a hallmark of a competent shop.
- Portfolio of Past Work: Reviewing previous projects can give insight into the quality and scope of work a shop can handle.
Importance of Certifications and Standards
Certifications like the ISO 9001 or AWS standards signal that a shop adheres to high-quality practices. They often provide confidence in the reliability and safety of fabricated products. Additionally, checking for industry-specific certifications can help ensure that the shop follows the required regulations and standards.
Cost Factors in Steel Fabrication
Average Pricing Breakdown
Understanding the average costs involved in steel fabrication can aid in budgeting.
Generally, costs for steel fabrication can range from $4 to $48 per square foot, depending on the complexity of the project, type of steel, and finish level required.
Customization and added functionalities often increase these costs.
Factors Affecting Costs
Several factors influence the cost of steel fabrication projects:
- Material Type: The type and grade of steel can significantly affect the price. Specialty steels tend to be more expensive due to their enhanced properties.
- Design Complexity: More intricate designs may require special tools and advanced techniques, contributing to higher costs.
- Volume of Production: Larger orders may benefit from economies of scale, lowering the per-unit cost.
Budgeting for Your Fabrication Project
Preparing a budget for your steel fabrication project involves considering all associated costs, including materials, labor, and additional services like shipping and installation. Planning for unexpected expenses and delays is also recommended, allowing greater flexibility and ensuring that projects are completed on time and within budget.
The Fabrication Process Explained
Steps Involved in Steel Fabrication
The steel fabrication process typically involves the following steps:
- Design Phase: Utilizing CAD software to create detailed schematics that outline how the final product will look.
- Material Selection: Choosing the appropriate steel type and grade based on the project’s specifications.
- Cutting: Using plasma or laser cutters to accurately cut the steel components to required dimensions.
- Bending and Forming: Employing hydraulic presses and rollers to form parts into their final shapes.
- Assembly and Welding: Joining components through welding or other methods to create the final product.
- Finishing: Applying coatings, paint, or treatments to protect against corrosion and improve aesthetics.
Tools and Technology Used
Modern steel fabrication relies on various tools and technologies to enhance precision and efficiency. Some commonly used equipment includes:
- CNC Machines: Computer-controlled machines like plasma cutters and laser cutters that ensure precision in cutting and shaping steel.
- Welding Equipment: TIG, MIG, and stick welders used for joining metal components securely while maintaining structural integrity.
- Press Breaks: Machines designed for bending metal sheets at precise angles.
Quality Control Measures in Fabrication
Implementing quality control measures throughout the fabrication process ensures that each finished product meets required standards. This can include regular inspections, testing welds, and verifying material integrity. Establishing a quality management system will improve consistency and reduce defects, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Materials Can Be Fabricated?
Steel fabrication primarily uses materials like stainless steel, aluminum, and mild steel, suitable for various applications.
How Long Does the Fabrication Process Take?
The timeline for fabrication varies based on project complexity, typically ranging from a few days to several weeks.
What Industries Utilize Steel Fabrication?
Industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing often rely on steel fabrication for essential components and structures.
How Can I Ensure Quality in Fabrication?
To ensure quality, request certifications, read reviews, and inquire about the shop’s quality control practices during the selection process.
What is the Environmental Impact of Steel Fabrication?
Many modern fabrication shops prioritize sustainable practices, focusing on material recycling and reducing waste during the fabrication processes.